Mobile robots should know where they are. Majority of the autonomous operation relies on constantly estimating the location and the orientation of the robot, that is, the pose of the robot.
Positioning can be described as the process of determining the pose of a robot relative to a given map of the environment. Mapping refers to the process of creating a consistent world model of the robot’s operating environment. Mapping is tightly coupled with positioning since creating a spatial model requires knowing the robot’s pose. A common approach for creating a world model is called Simultaneous Localisation and Mapping (SLAM).
Most positioning and mapping solutions rely on sensor fusion, that is, combining data from various types of sensors. Sensor fusion requires that all the sensor data can be transformed into a single frame of reference and time instant. This requires knowing the relative positions, orientation, and synchronisation offsets of the sensors with respect to each other’s. Estimating these parameters is called extrinsic calibration.

GIM products offer a solution for the three fundamental problems in robotics: calibration, mapping, and positioning. Our localisation related solutions are shortly described next.
MITTA – Calibration Tool
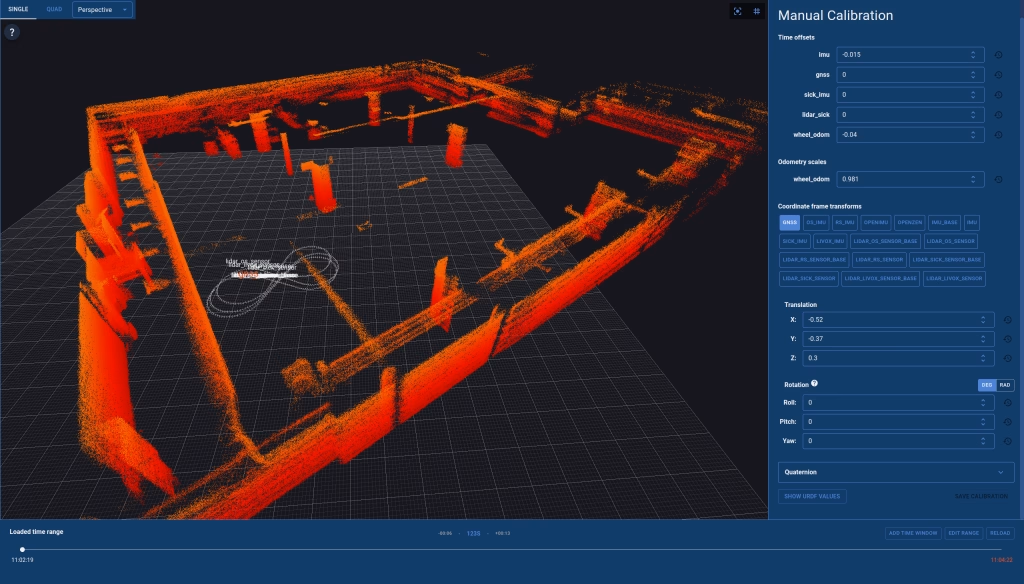
MITTA is a browser-based calibration tool. The user interface enables users to find the three-dimensional (3D) extrinsic calibration parameters for a mobile robot using recorded sensor data. MITTA has been designed to visualise 3D point cloud data intuitively for the users. MITTA facilitates the calibration process by providing an intuitive visualisation of 3D point cloud data and all necessary controls. It also employs advanced optimisation algorithms to determine the optimal calibration parameters.
Calibration is a preprocessing step that needs to be done once for every machine as a deployment step. Recalibration is only needed if there is some change in the sensor setup.
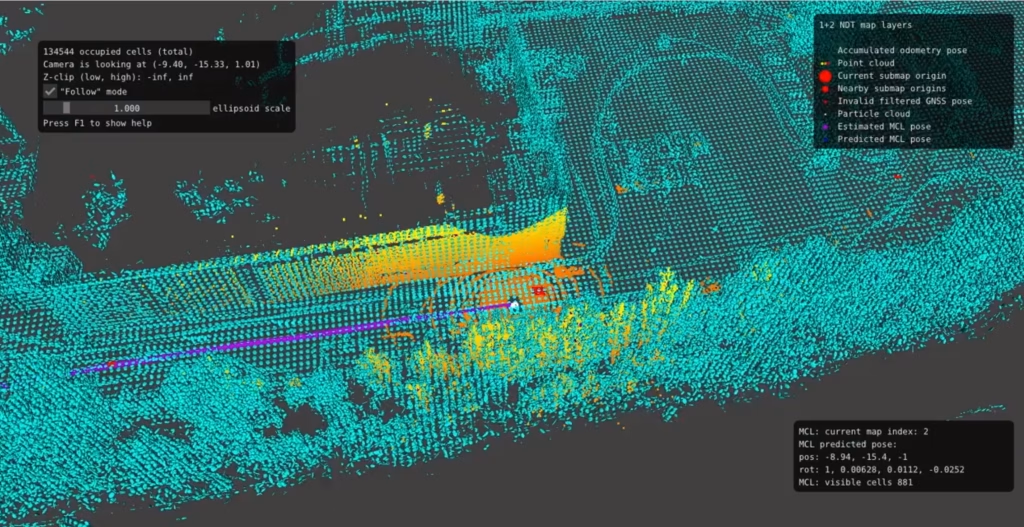
KARTTA – Map Creation and Validation Tool
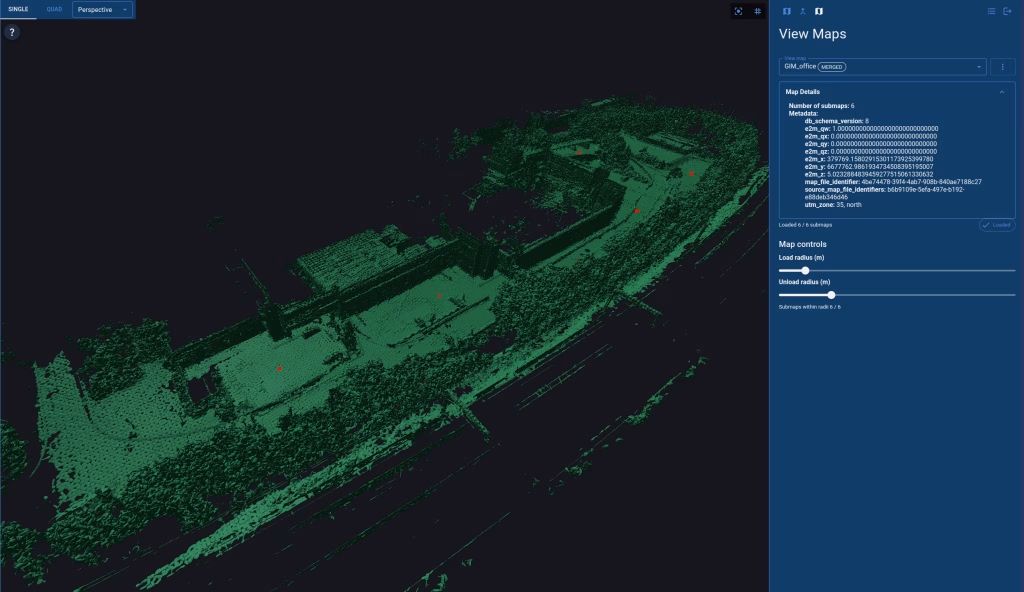
KARTTA is a map creation and validation tool. It is a browser-based user interface for creating geometric three-dimensional (3D) maps from recorded sensor data. These maps can be used for robust real-time positioning when operating in the same environment. The maps are compatible with PAIKKA, a map-based positioning software by GIM Robotics.
Map creation is a preprocessing step that must be performed at least once at every operating area before positioning can be initiated. The generated maps must cover the whole area of operation. Calibration parameters must be known before map creation.
PAIKKA – 3D Positioning Solution
PAIKKA is a sophisticated 3D positioning solution for mobile robots. PAIKKA provides infrastructure- and GNSS-free all-weather conditions solution for indoor and outdoor 3D positioning in real-time. The accurate pose estimates enable improving the safety, efficiency, and precision of the operations by increasing the level of autonomy.
PAIKKA is a map-based positioning system, and the pose estimates are given with reference to a map. If the map is in global coordinates such as GNSS, then the pose estimate is given in global coordinates.
Using PAIKKA requires a geometric 3D map of the operating environment. Furthermore, accurate sensor calibration and synchronisation is a requirement for PAIKKA usage.
The architecture
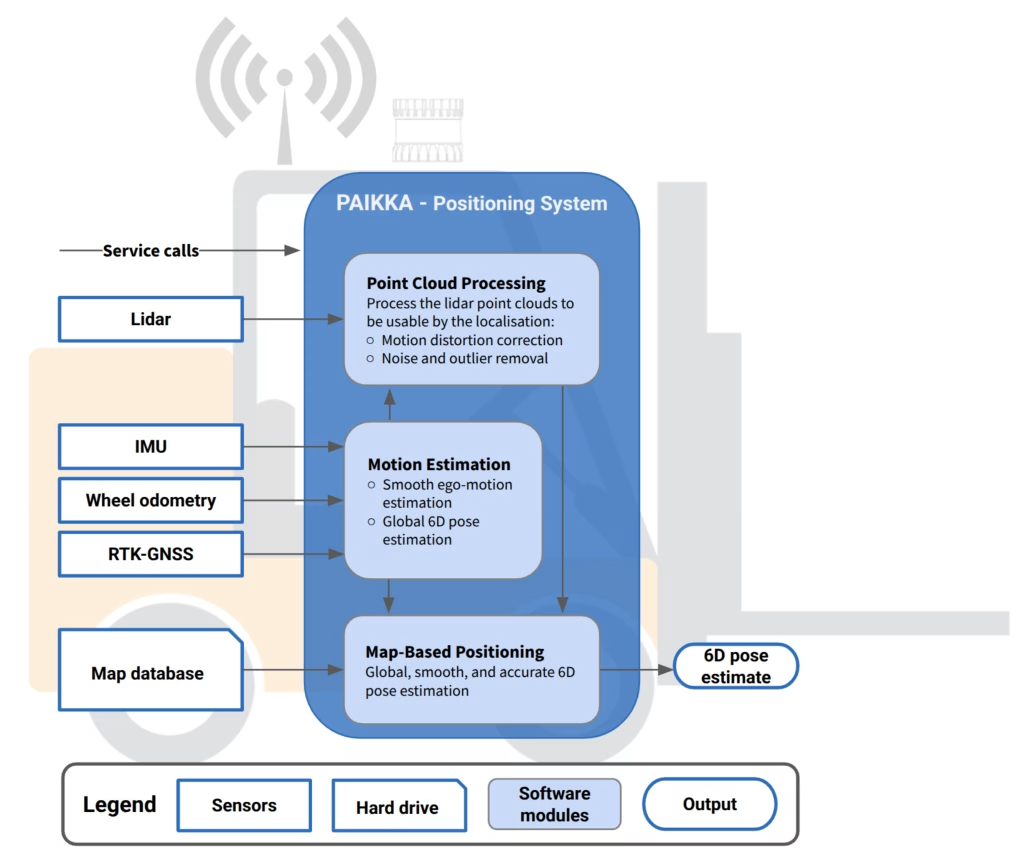
PAIKKA delivers robust 3D pose estimates for mobile machines. The positioning system operates real-time on an Industrial PC mounted onto the mobile platform, ensuring continuous and precise positioning in real-world scenarios.
- Motion estimation module fuses IMU, odometry, and GNSS receiver data to estimate the vehicle’s ego-motion.
- Point cloud processing module produces high quality point cloud data by exploiting the ego-motion estimates for compensating the distortions in the point cloud caused by the platform movement.
- Map-based positioning module estimates the output pose using the ego-motion estimate, rectified point cloud data, and the environment representation generated in the mapping stage.
The high-level architecture of PAIKKA can be seen below in Figure 4.
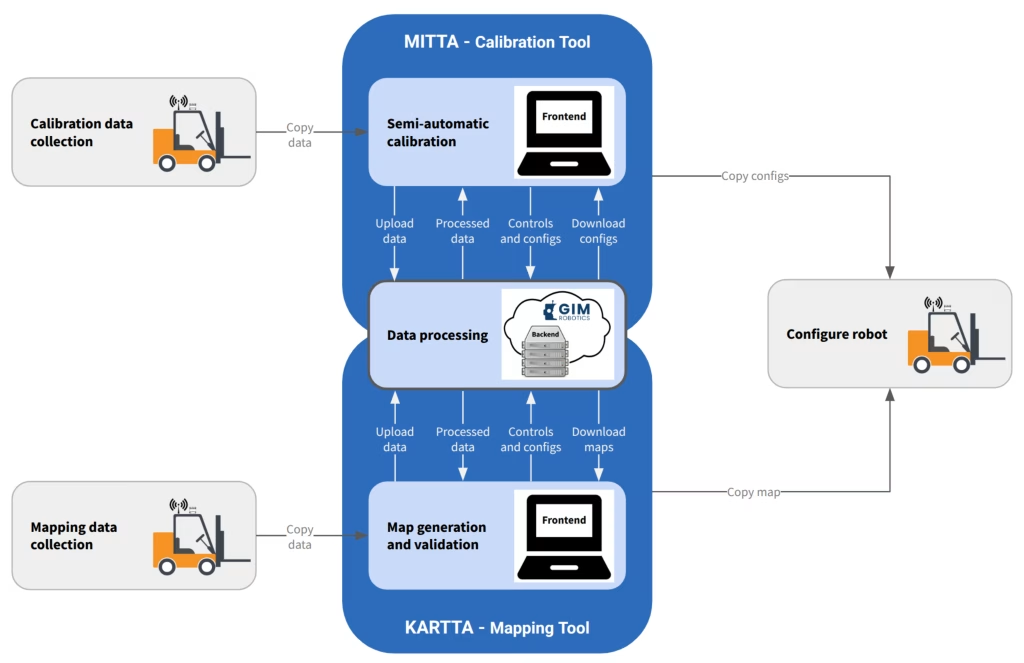
The geometric 3D map required by PAIKKA can be created with KARTTA, that is, a map creation and validation tool. However, both KARTTA and PAIKKA use advanced sensor fusion methods. Successful sensor fusion requires accurate calibration and synchronisation between all the involved sensor modalities. These parameters can be estimated with MITTA, that is, browser-based calibration tool by GIM Robotics. Both MITTA and KARTTA are offline tools that process recorded sensor data. Figure 6 illustrates the workflow with MITTA and KARTTA tools.